Periodic table of elements quiz 1 36 – Periodic Table of Elements Quiz 1-36 embarks on an exciting journey into the realm of chemistry, unraveling the secrets of the first 36 elements that shape our world. From their fundamental properties to their diverse applications, this quiz will illuminate the building blocks of matter and inspire a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of the periodic table.
Delving into the chemical properties of these elements, we will explore their reactivity, electronegativity, and other defining characteristics. The organization of the periodic table will be meticulously examined, revealing the patterns and trends that govern the behavior of elements. Furthermore, we will uncover the historical discoveries that led to the development of the periodic table, paying homage to the brilliant minds who shaped our understanding of the elements.
Periodic Table of Elements Quiz 1-36
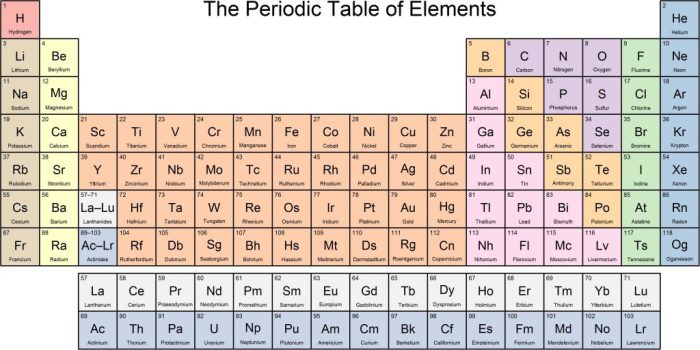
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. It is generally accepted that the modern periodic table was first published by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, although several other scientists had developed similar tables prior to this.
The periodic table has been arranged so that elements with similar properties are grouped together. The rows of the table are called periods, and the columns are called groups. The periodic table can be used to predict the properties of an element based on its position in the table.
Periodic Table of Elements 1-36, Periodic table of elements quiz 1 36
The following table lists the first 36 elements of the periodic table, along with their atomic numbers, names, and symbols:
| Atomic Number | Name | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hydrogen | H |
| 2 | Helium | He |
| 3 | Lithium | Li |
| 4 | Beryllium | Be |
| 5 | Boron | B |
| 6 | Carbon | C |
| 7 | Nitrogen | N |
| 8 | Oxygen | O |
| 9 | Fluorine | F |
| 10 | Neon | Ne |
| 11 | Sodium | Na |
| 12 | Magnesium | Mg |
| 13 | Aluminum | Al |
| 14 | Silicon | Si |
| 15 | Phosphorus | P |
| 16 | Sulfur | S |
| 17 | Chlorine | Cl |
| 18 | Argon | Ar |
| 19 | Potassium | K |
| 20 | Calcium | Ca |
| 21 | Scandium | Sc |
| 22 | Titanium | Ti |
| 23 | Vanadium | V |
| 24 | Chromium | Cr |
| 25 | Manganese | Mn |
| 26 | Iron | Fe |
| 27 | Cobalt | Co |
| 28 | Nickel | Ni |
| 29 | Copper | Cu |
| 30 | Zinc | Zn |
| 31 | Gallium | Ga |
| 32 | Germanium | Ge |
| 33 | Arsenic | As |
| 34 | Selenium | Se |
| 35 | Bromine | Br |
| 36 | Krypton | Kr |
Element Properties
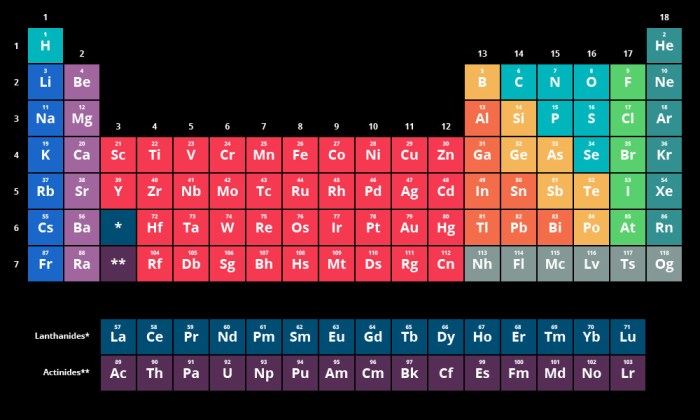
The chemical properties of the first 36 elements are determined by their electronic configurations. The number of electrons in the outermost shell, known as the valence electrons, plays a crucial role in determining the element’s reactivity, electronegativity, and other characteristics.
Reactivity
Reactivity refers to the tendency of an element to undergo chemical reactions. The more reactive an element is, the more readily it will react with other elements. The reactivity of the first 36 elements generally increases down a group (column) and decreases across a period (row) of the periodic table.
- Alkali metals (Group 1) are highly reactive due to their single valence electron, which they readily lose to achieve a stable octet configuration.
- Halogens (Group 17) are also highly reactive, but they gain electrons to achieve a stable octet configuration.
- Noble gases (Group 18) are the least reactive elements because they have a stable octet configuration and do not tend to gain or lose electrons.
Electronegativity
Electronegativity is a measure of an element’s ability to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond. The higher the electronegativity, the more strongly an element attracts electrons.
Electronegativity generally increases across a period and decreases down a group of the periodic table.
- Fluorine (F) is the most electronegative element, with an electronegativity of 4.0.
- Cesium (Cs) is the least electronegative element, with an electronegativity of 0.79.
Other Relevant Characteristics
In addition to reactivity and electronegativity, other relevant characteristics of the first 36 elements include:
- Metallic character:Metals are generally shiny, malleable, and ductile. Metallic character increases down a group and decreases across a period.
- Non-metallic character:Non-metals are generally dull, brittle, and poor conductors of electricity. Non-metallic character increases across a period and decreases down a group.
- Oxidation states:The oxidation state of an element refers to the number of electrons it can gain or lose in a chemical reaction. The most common oxidation states for the first 36 elements are +1, +2, +3, and -1.
Element Organization
The periodic table is organized based on the atomic number of the elements, which is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. The elements are arranged in rows (called periods) and columns (called groups) based on their atomic number and their chemical properties.
The first 36 elements are organized as follows:
- The first period contains two elements: hydrogen and helium.
- The second period contains eight elements: lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon.
- The third period contains eight elements: sodium, magnesium, aluminum, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, and argon.
- The fourth period contains eight elements: potassium, calcium, scandium, titanium, vanadium, chromium, manganese, and iron.
Trends in Atomic Number
The atomic number of the elements increases from left to right across a period and from top to bottom down a group.
Trends in Atomic Mass
The atomic mass of the elements generally increases from left to right across a period and from top to bottom down a group.
Trends in Electron Configuration
The electron configuration of the elements follows a pattern as you move across a period and down a group. The electron configuration of an element determines its chemical properties.
Element Applications
The first 36 elements on the periodic table have a wide range of applications in everyday life, spanning industries, medicine, and technology.
These elements play crucial roles in various products and processes that we encounter daily, from the food we eat to the devices we use.
Industrial Applications
- Iron (Fe):Used in steel production, construction, and transportation.
- Copper (Cu):Employed in electrical wiring, plumbing, and electronics.
- Aluminum (Al):Used in aerospace, construction, and packaging.
- Calcium (Ca):Essential for bone health and used in cement production.
- Sodium (Na):Found in table salt and used in food preservation and industrial processes.
Medical Applications
- Hydrogen (H):Used in medical imaging and fuel cells.
- Oxygen (O):Vital for respiration and used in medical treatments.
- Nitrogen (N):Found in fertilizers and used in cryopreservation.
- Phosphorus (P):Essential for bone health and used in dental materials.
- Iodine (I):Used in antiseptics and thyroid medications.
Technological Applications
- Silicon (Si):Used in semiconductors and computer chips.
- Titanium (Ti):Used in aerospace, medical implants, and jewelry.
- Zinc (Zn):Used in galvanization, batteries, and alloys.
- Bromine (Br):Used in fire retardants and photography.
- Argon (Ar):Used in lighting and welding.
Element History: Periodic Table Of Elements Quiz 1 36
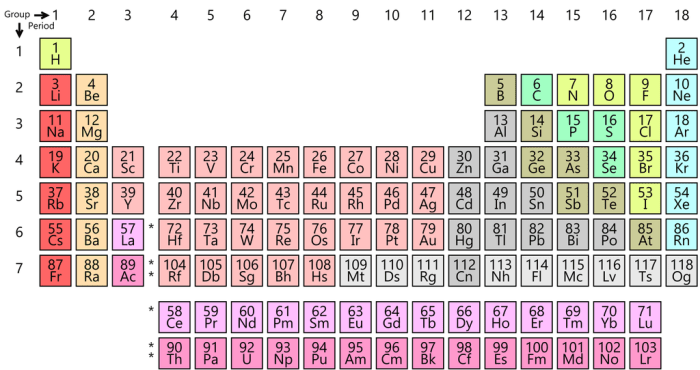
The study of the elements and their properties has a long and fascinating history. The first elements to be discovered were gold, silver, copper, and iron, which were known to ancient civilizations. These elements were used to make tools, weapons, and jewelry.
In the 18th century, scientists began to develop new methods for identifying and classifying elements. In 1789, Antoine Lavoisier published a list of 33 elements, which he divided into metals, non-metals, and gases. This list was the first step in the development of the periodic table.
Scientists and their Contributions
Many scientists have contributed to the development of the periodic table. Some of the most important include:
- Antoine Lavoisier: French chemist who published the first list of elements in 1789.
- Jöns Jakob Berzelius: Swedish chemist who developed a system for naming and classifying elements.
- Dmitri Mendeleev: Russian chemist who published the first periodic table in 1869.
- Henry Moseley: English physicist who discovered the atomic number of elements.
The periodic table has been revised and expanded over time as new elements have been discovered. The modern periodic table contains 118 elements, which are arranged in order of their atomic number.
Helpful Answers
What is the atomic number of oxygen?
8
Which element is known for its high reactivity?
Sodium
Who is credited with developing the periodic table?
Dmitri Mendeleev