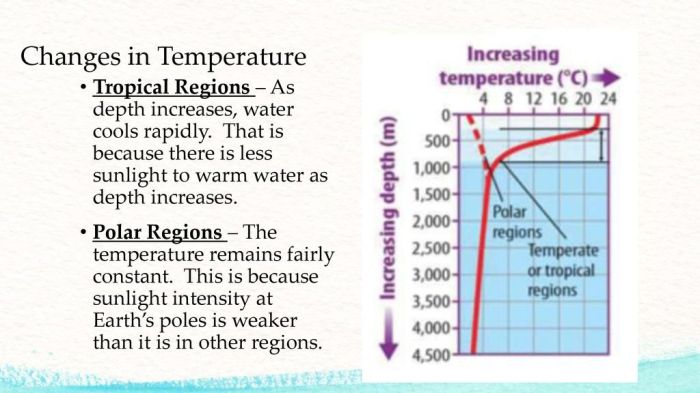
Polar and tropical regions maintain fairly constant average temperatures because of several factors, including the Earth’s tilt, atmospheric circulation, and ocean currents. These factors combine to create unique and stable ecosystems in both polar and tropical regions, supporting diverse plant and animal life.
The Earth’s tilt on its axis causes the amount of solar radiation reaching different parts of the planet to vary throughout the year. This variation in solar radiation is responsible for the seasons we experience in temperate regions. However, the polar and tropical regions are less affected by seasonal changes due to their constant exposure to either high or low levels of solar radiation.
Polar and Tropical Temperature Regulation: Polar And Tropical Regions Maintain Fairly Constant Average Temperatures Because
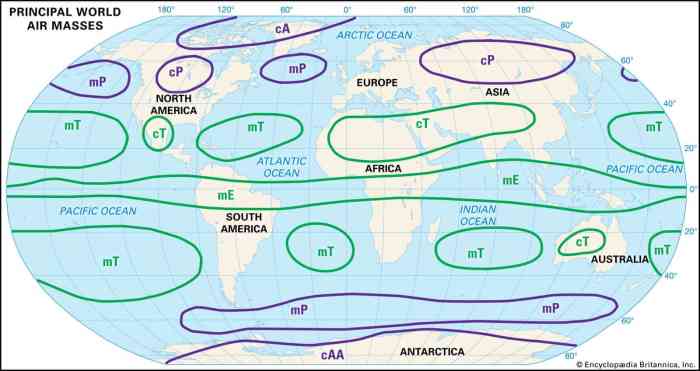
Polar and tropical regions exhibit relatively constant average temperatures due to several factors:
Earth’s Tilt and Solar Radiation:The Earth’s axis of rotation is tilted, resulting in varying amounts of solar radiation reaching different regions throughout the year. Polar regions receive less direct sunlight, leading to colder temperatures. Conversely, tropical regions receive more direct sunlight, resulting in warmer temperatures.
Atmospheric Effects:The Earth’s atmosphere plays a crucial role in regulating temperatures. In polar regions, the atmosphere is thinner, allowing more heat to escape into space. In tropical regions, the atmosphere is thicker, trapping more heat and leading to higher temperatures.
Ocean Currents:Ocean currents significantly influence temperature distribution. Warm currents, such as the Gulf Stream, carry heat from tropical regions towards polar regions, moderating their temperatures. Conversely, cold currents, such as the Humboldt Current, carry cold water from polar regions towards tropical regions, lowering their temperatures.
Impact on Local Ecosystems
Constant temperatures in polar and tropical regions have a profound impact on local ecosystems:
- Adaptations of Plants and Animals:Organisms in these regions have evolved adaptations to withstand the stable temperatures. Polar animals, such as polar bears and penguins, have thick fur and blubber for insulation. Tropical plants and animals often have large leaves and thin bark to maximize sunlight absorption and reduce heat stress.
- Species Diversity and Ecological Balance:The lack of temperature variation in these regions affects species diversity and ecological balance. Polar regions support fewer species due to the harsh conditions, while tropical regions exhibit higher species diversity due to the stable and favorable temperatures.
- Unique Challenges:Organisms in these environments face unique challenges. Polar organisms must cope with extreme cold and lack of sunlight, while tropical organisms must adapt to high temperatures and humidity.
- Thermometers and Sensors:Traditional thermometers and electronic sensors are used to measure temperatures in both regions. Polar regions require specialized thermometers designed to withstand extreme cold, while tropical regions use thermometers suitable for high temperatures and humidity.
- Challenges of Data Collection:Collecting accurate temperature data in extreme environments can be challenging. Polar regions experience extreme cold and limited accessibility, while tropical regions face high humidity and dense vegetation.
- Remote Sensing and Satellite Technology:Remote sensing and satellite technology play a crucial role in temperature monitoring in these regions. Satellites equipped with thermal sensors can measure temperatures from space, providing valuable data for inaccessible areas.
- Impacts on Ecosystems:Altering temperature patterns can disrupt local ecosystems, leading to species loss and habitat destruction.
- Weather Patterns:Changes in temperature can affect weather patterns, resulting in more extreme weather events such as hurricanes and droughts.
- Human Populations:Altered temperature patterns can impact human populations, affecting health, agriculture, and access to resources.
- Biodiversity:Temperature changes can reduce biodiversity by affecting the survival and reproduction of species.
- Sea Level Rise:Altering temperature patterns can lead to sea level rise due to the melting of polar ice caps.
- Global Climate Patterns:Changes in temperature in polar and tropical regions can disrupt global climate patterns, affecting weather systems worldwide.
Methods for Measuring and Monitoring Temperatures, Polar and tropical regions maintain fairly constant average temperatures because
Measuring and monitoring temperatures in polar and tropical regions require different approaches:
Key Differences in Temperature Regulation
| Polar Regions | Tropical Regions |
|---|---|
| Less direct sunlight due to Earth’s tilt | More direct sunlight due to Earth’s tilt |
| Thinner atmosphere allows heat to escape | Thicker atmosphere traps heat |
| Cold ocean currents carry cold water from polar regions | Warm ocean currents carry heat from tropical regions towards polar regions |
| Lower species diversity due to harsh conditions | Higher species diversity due to stable temperatures |
| Polar animals have thick fur and blubber for insulation | Tropical plants and animals have large leaves and thin bark |
Consequences of Altering Temperature Patterns
Essential Questionnaire
Why are the polar regions so cold?
The polar regions are cold because they receive less solar radiation than the tropical regions. This is due to the Earth’s tilt on its axis, which causes the sun’s rays to be more concentrated at the equator.
Why are the tropical regions so warm?
The tropical regions are warm because they receive more solar radiation than the polar regions. This is due to the Earth’s tilt on its axis, which causes the sun’s rays to be more concentrated at the equator.
How do ocean currents affect the temperature of polar and tropical regions?
Ocean currents can transport warm or cold water from one region of the globe to another. This can have a significant impact on the temperature of the regions that the currents flow through.